Difference between revisions of "Main Page"
(Update to expand page and include more elements) |
m |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
<p>[[Rotators|Rotators]]</p> | <p>[[Rotators|Rotators]]</p> | ||
<p>[[Antennas|Antennas]]</p> | <p>[[Antennas|Antennas]]</p> | ||
| − | <p>[[Receiver| | + | <p>[[Receiver|Signal Reception]]</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div style="border-radius: 3px; width: 25%; height: 200px; background-color: #f6f6f6; float: left; display: block; margin: 1.5%; border: 1px solid #A7D7F9; text-align: center; padding: 2.5%; padding-top: 0px;"> | <div style="border-radius: 3px; width: 25%; height: 200px; background-color: #f6f6f6; float: left; display: block; margin: 1.5%; border: 1px solid #A7D7F9; text-align: center; padding: 2.5%; padding-top: 0px;"> | ||
Revision as of 11:45, 4 December 2017
SatNOGS is an integral part of the Libre Space Foundation [1]. The project aims to build a global network of satellite ground stations. Designed as an open source participatory project which is straightforward to build using commonly available parts and some 3D printed elements. A ground station is built to interact with a website that holds key satellite information. The web interface allows a user to schedule a satellite observation of any of the networked ground stations.
Here you can find more information on how to get started with SatNOGS, building and operating a satellite ground station and joining the SatNOGS Network.
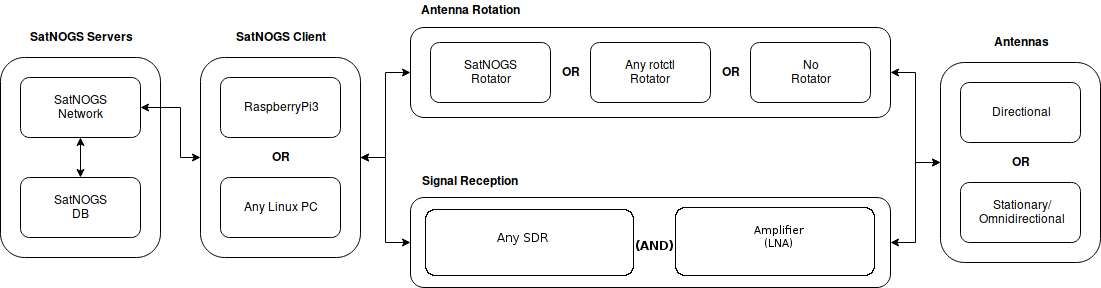
A SatNOGS ground station can be made in a variety of ways. The reference design uses a Raspberry Pi and RTL-SDR dongle with either stationary antennas or either a SatNOGS rotator or a commercial amateur radio rotator. There is provision to use amateur radio transceivers or alternative SDR technology. The image below explains the system.The image below explains the system.
Contents
What is SatNOGS
Operate