Difference between revisions of "Introduction"
(categories) |
(Added two presentations) (Tag: Visual edit) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <p>SatNOGS project is a complete platform of an Open Source Networked Ground Station. The scope of the project is to create a full stack of open technologies based on open standards , and the construction of a full ground station as a showcase of the stack.</p> | + | <p>SatNOGS project is a complete platform of an Open Source Networked Ground Station. The scope of the project is to create a full stack of open technologies based on open standards, and the construction of a full ground station as a showcase of the stack.</p> |
<p>SatNOGS provides the basis for:</p> | <p>SatNOGS provides the basis for:</p> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
<h3>Ground Stations:</h3> | <h3>Ground Stations:</h3> | ||
<p>A ground station is considered to be exactly as the name suggests. It is a receiver and antenna combination connected to the SatNOGS Global Management Network with some form of computer. There are two main types of ground stations, these are:</p> | <p>A ground station is considered to be exactly as the name suggests. It is a receiver and antenna combination connected to the SatNOGS Global Management Network with some form of computer. There are two main types of ground stations, these are:</p> | ||
| − | <p><em><strong>Fixed or Non-Rotator</strong></em> | + | <p><em><strong>Fixed or Non-Rotator</strong></em> — i.e. their antennas wait for the satellites to pass over them (These are simpler types and commonly have a Raspberry Pi and RTL-SDR combination coupled to an antenna like a Turnstile, Eggbeater or other similar fixed antenna type) or</p> |
| − | <p><em><strong>Steerable or Rotator</strong></em> | + | <p><em><strong>Steerable or Rotator</strong></em> — i.e. they point a yagi antenna at the satellite and track it as it passes overhead. These stations can use the simpler Raspberry Pi and RTL-SDR combination but need a rotator such as the SatNOGS rotator or a commercial alternative.</p> |
<h3>Satellites:</h3> | <h3>Satellites:</h3> | ||
<p>Simply any satellite in the SatNOGS Database. This is a growing record of educational, amateur and commercial satellites commonly referred to as the DB.</p> | <p>Simply any satellite in the SatNOGS Database. This is a growing record of educational, amateur and commercial satellites commonly referred to as the DB.</p> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
<h3>Presentations on SatNOGS</h3> | <h3>Presentations on SatNOGS</h3> | ||
| − | Dan White presented [https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2018/all2018/313/ | + | * Alfredos Panagiotis Damkalis presented [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ltqgCXi5SGs "SatNOGS - State of the Union"] at [https://indico.oscw.space/event/3/contributions/62/ OSCW 2019]. |
| + | * Corey Shields & Dan White presented a workshop on [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DrgsOxZEq9o "SatNOGS Ground Station Building Guide"] at TAPR DCC 2019 | ||
| + | * Dan White presented [https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/smallsat/2018/all2018/313/ “Overview of the Satellite Networked Open Ground Stations (SatNOGS) Project”] at 32nd SmallSat conference 2018. | ||
| + | * Nikos Roussos presented [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fxKCWNXFh2g “SatNOGS: Crowd-sourced satellite operations Satellite Open Source Ground Station Network”] at FOSDEM 2018. | ||
| + | * Pierros Pappadeas presented [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JGv-S1F-hQo "Going to space the Libre way”] at the AMSAT UK RSGB 2017 convention. | ||
| + | * Scott Bragg presented [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BKULw0NXhyI "Decoding Satellites with SatNOGS"] at linux.conf.au in 2017. | ||
| + | * Manolis Surligas presented [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zs_J1wlIpMs "SatNOGS: An SDR-based Satellite Networked Open Ground Station"] at FOSDEM 2017. | ||
| + | * Dan White presented "SatNOGS: Satellite Networked Ground Stations" at the Digital Communications Conference in 2015. | ||
| − | + | ==See also== | |
| − | + | *[[Academic Papers]] on SatNOGS. | |
| − | + | *[https://satnogs.org/faq/ SatNOGS FAQ]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Build]] | [[Category:Build]] | ||
| Line 47: | Line 46: | ||
[[Category:Hardware]] | [[Category:Hardware]] | ||
[[Category:Software]] | [[Category:Software]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Community]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:17, 4 August 2020
SatNOGS project is a complete platform of an Open Source Networked Ground Station. The scope of the project is to create a full stack of open technologies based on open standards, and the construction of a full ground station as a showcase of the stack.
SatNOGS provides the basis for:
- Bulk manufacturing and deployment of affordable Satellite Ground Stations
- Modular design for integration with existing and future technologies
- A platform for a variety of instrumentation around Satellite Ground Station operations
- A firm platform for a Ground Station collaborative network (one to one, one to many, many to many)
- A community based approach on Ground Station development
- A solution for massive automation of operator-less Ground Stations based on open standards
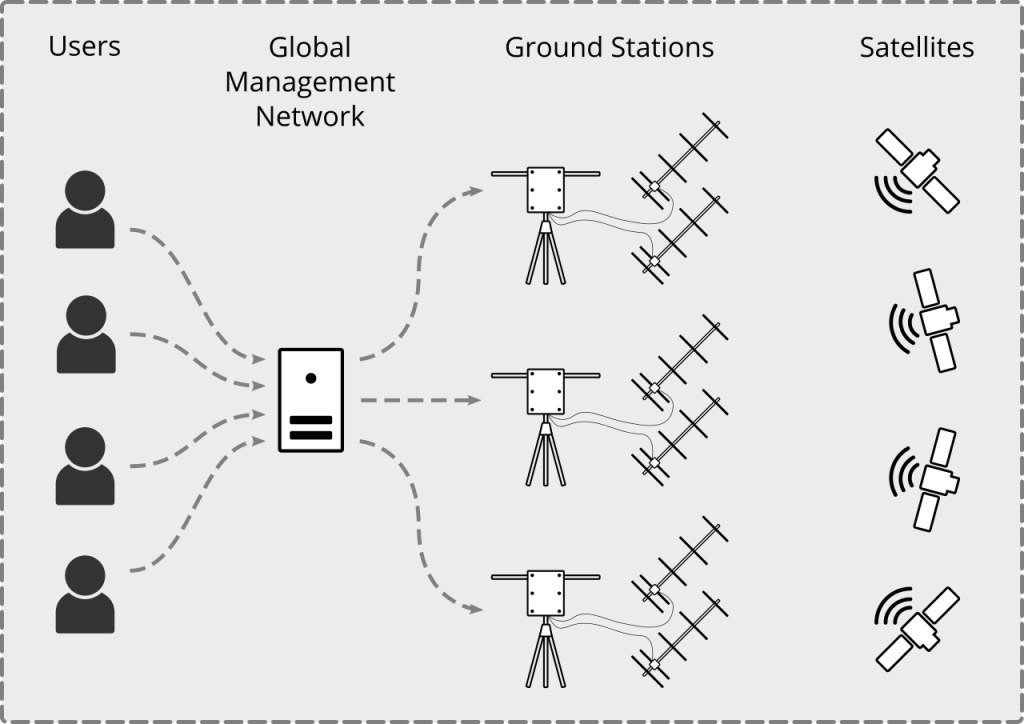
There are a number of elements to the project that integrate hardware and software in a way that allows multiple observers to be connected to multiple ground stations so that tracking and monitoring satellites from multiple locations is possible. The data that is collected is publically available through the production environment.
At the centre is the global management network consisting of:
Contents
Users:
A user is any validated member of the SatNOGS system. All you need is to sign up and with a bit of familiarity you will be able to use the system.
Global Management Network:
SatNOGS Network – Our observations, scheduling and discovery server. SatNOGS Network is a web application for scheduling observations across the network of ground stations. It facilitates the coordination of satellite signal observations, and scheduling such observations among the satellite ground-stations connected on the network.
SatNOGS Client – An embedded system that receives the scheduled operation from Network, records an observation and sends it back. SatNOGS Client is the software to run on ground stations, usually on embedded systems, that receives the scheduled observations from the Network, receives the satellite transmission and sends it back to the Network web app.
SatNOGS Ground Station – The actual ground station instrumentation with tracker, antennas, LNAs and connected to Client. SatNOGS Ground Station is an open source hardware ground station instrumentation with a rotator, antennas, electronics and connected to the Client. It is based on 3D printed components and readily available materials.
Ground Stations:
A ground station is considered to be exactly as the name suggests. It is a receiver and antenna combination connected to the SatNOGS Global Management Network with some form of computer. There are two main types of ground stations, these are:
Fixed or Non-Rotator — i.e. their antennas wait for the satellites to pass over them (These are simpler types and commonly have a Raspberry Pi and RTL-SDR combination coupled to an antenna like a Turnstile, Eggbeater or other similar fixed antenna type) or
Steerable or Rotator — i.e. they point a yagi antenna at the satellite and track it as it passes overhead. These stations can use the simpler Raspberry Pi and RTL-SDR combination but need a rotator such as the SatNOGS rotator or a commercial alternative.
Satellites:
Simply any satellite in the SatNOGS Database. This is a growing record of educational, amateur and commercial satellites commonly referred to as the DB.
SatNOGS DB – Our crowd-sourced suggestions transponder info website. SatNOGS Database is a crowd-sourced application allowing its users to suggest satellite transmitter information for currently active satellites. Its data are available via an API or via a web application interface, allowing other project to use its satellite transmitter information.
Presentations on SatNOGS
- Alfredos Panagiotis Damkalis presented "SatNOGS - State of the Union" at OSCW 2019.
- Corey Shields & Dan White presented a workshop on "SatNOGS Ground Station Building Guide" at TAPR DCC 2019
- Dan White presented “Overview of the Satellite Networked Open Ground Stations (SatNOGS) Project” at 32nd SmallSat conference 2018.
- Nikos Roussos presented “SatNOGS: Crowd-sourced satellite operations Satellite Open Source Ground Station Network” at FOSDEM 2018.
- Pierros Pappadeas presented "Going to space the Libre way” at the AMSAT UK RSGB 2017 convention.
- Scott Bragg presented "Decoding Satellites with SatNOGS" at linux.conf.au in 2017.
- Manolis Surligas presented "SatNOGS: An SDR-based Satellite Networked Open Ground Station" at FOSDEM 2017.
- Dan White presented "SatNOGS: Satellite Networked Ground Stations" at the Digital Communications Conference in 2015.
See also
- Academic Papers on SatNOGS.
- SatNOGS FAQ.