Difference between revisions of "SatNOGS Monitor"
Alexcj2802 (talk | contribs) (Added a link to the creator's forked version of yaft, which uses the Lucy Tewi font by default. https://github.com/wose/yaft) (Tag: Visual edit) |
(categories) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == | + | == Introduction == |
[[File:Satnogs-monitor.png|800px]] | [[File:Satnogs-monitor.png|800px]] | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
edit ~/.config/satnogs-monitor/config.toml | edit ~/.config/satnogs-monitor/config.toml | ||
cargo run --release -- -s 175 | cargo run --release -- -s 175 | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Operation]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Software]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Develop]] | ||
Revision as of 22:43, 19 January 2020
Contents
Introduction
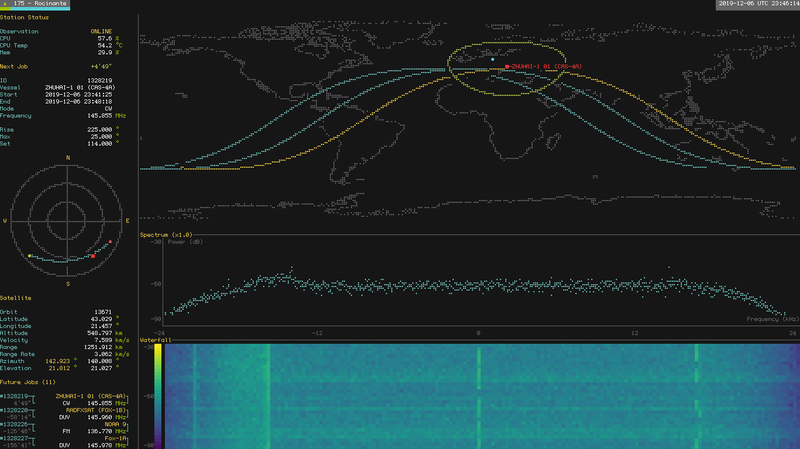
SatNOGS Monitor is a terminal ui to monitor your and/or other ground stations of the SatNOGS network. It is written in Rust and runs on Linux and has been reported to run on MacOS[1]. Windows is currently not supported by the underlying terminal library, but might be added at some point in the future. SatNOGS Monitor does not need to be installed on an actual SatNOGS station computer (although there are benefits to doing so as discussed below).
Installation
Dependencies
SatNOGS Monitor uses bindings to libgpredict[2]. This library is not available as installable package and you'll have to build it yourself.
Install libgpredict dependencies
sudo apt-get install libglib2.0-dev cmake build-essential git
Build and install libgpredict
git clone https://github.com/cubehub/libgpredict.git cd libgpredict mkdir build cd build cmake ../ make sudo make install sudo ldconfig # for linux
Raspberry Pi (armhf)
You can run the SatNOGS Monitor on the same Raspberry Pi as your ground station. You'll need to build and install libgpredict as shown above and can build the monitor from source (see [#Hacking]) or use the prebuild Raspbian package.
wget https://github.com/wose/satnogs-monitor/releases/download/0.3.1/satnogs-monitor_0.3.1_armhf.deb sudo dpkg -i satnogs-monitor_0.3.1_armhf.deb
You can then run the monitor over any ssh connection to your ground station or view it directly on a display attached to your RPi. See this thread for some inspiration.
Linux (x86_64)
If you're running an Debian like distribution you can install the prebuild package after building and installing libgpredict.
wget https://github.com/wose/satnogs-monitor/releases/download/0.3.1/satnogs-monitor_0.3.1_amd64.deb sudo dpkg -i satnogs-monitor_0.3.1_amd64.deb
See [#Hacking] if you're running another distribution.
Running it
The monitor makes heavy usage of braille unicode characters so make sure your terminal emulator uses a font which includes those glyphs. The screenshot at the top shows alacritty[3] with the tewi-font[4]. Take a look at nerd-fonts[5] if you're unsure about which font to use. You could also use a forked version of yaft[6] created by the same person as SatNOGS Monitor, which uses the Lucy Tewi font by default.
Monitor single station:
satnogs-monitor -s 175
Multiple stations:
satnogs-monitor -s 175 -s 227
Monitor a station on the same machine as the monitor runs (gets you more system infos):
satnogs-monitor -l 175
Monitor a local station and multiple remote stations:
satnogs-monitor -l 175 -s 227 -s 2
If satnogs-montor runs on the same machine as satnogs-client (typically a Raspberry Pi) you can set the satnogs client data path and enable the spectrum and/or waterfall plot to get a visualization of the received signal of the current observation.
satnogs-monitor -l 175 --data-path /tmp/.satnogs/data/ --waterfall --spectrum
If you have a rotator setup you can monitor the current rotator position by configuring the rotctld address:
satnogs-monitor -l 175 --rotctld-address 127.0.0.1:4533
You can also create a config file with all those informations:
mkdir ~/config/satnogs-monitor cd ~/config/satnogs-monitor wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wose/satnogs-monitor/master/monitor/examples/config.toml edit config.toml
Check the help for more command line arguments:
$ satnogs-monitor -h
satnogs-monitor 0.3.1
Monitors the current and future jobs of SatNOGS ground stations.
USAGE:
satnogs-monitor [FLAGS] [OPTIONS]
FLAGS:
-h, --help Prints help information
--spectrum Enables the spectrum plot
-V, --version Prints version information
-v Sets the level of log verbosity
--waterfall Enables the waterfall plot
OPTIONS:
-a, --api <URL> Sets the SatNOGS network api endpoint url
-c, --config <FILE> Sets custom config file
--data-path <PATH> Enables the spectrum and waterfall plot if set to the SatNOGS
client data path (/tmp/.satnogs/data/)
--db-max <DB> Sets the upper dB bound of the spectrum and waterfall plot
(0)
--db-min <DB> Sets the lower dB bound of the spectrum and waterfall plot
(-100)
-l, --local <ID>... Adds a station running on the same machine as this monitor
with this SatNOGS network id to to the list of monitored
stations
-o, --orbits <NUM> Sets the number of orbits plotted on the map
--rotctld-address <IP:PORT> Enables rotator monitoring if set to a rotctld address
-s, --station <ID>... Adds a station with this SatNOGS network id to the list of
monitored stations
--waterfall-zoom <FACTOR> Zooms the spectrum and waterfall plot (1.0 - 10.0)
TAB key will cycle through available stations while SatNOGS Monitor is running.
Hacking
To build the monitor from source you'll need to install the Rust. Use your package manager or follow this site.
git clone https://github.com/wose/satnogs-monitor.git cd satnogs-monitor/monitor mkdir ~/.config/satnogs-monitor cp examples/config.toml ~/.config/satnogs-monitor/ edit ~/.config/satnogs-monitor/config.toml cargo run --release -- -s 175